
Top Security Mistakes Companies Make During Atlassian Cloud Migration (And How to Avoid Them)
Top Security Mistakes Companies Make During Atlassian Cloud Migration (And How to Avoid Them)
Migrating from Atlassian Data Center to Cloud is not just a technical upgrade, it’s a strategic move that can either future-proof your business or expose it to unforeseen risks. For decision-makers and enterprises still operating in Data Center, the clock is ticking: Atlassian’s push toward cloud-first architecture means migration is no longer optional, but inevitable.
Yet security remains the #1 concern for enterprises making this transition. This post will explore the most common and costly security mistakes companies make during Atlassian Cloud migration, backed by real-world examples and actionable solutions.
Why Security Matters in Atlassian Cloud Migration
Atlassian Cloud offers unparalleled scalability, AI-driven innovations, and reduced maintenance burdens. However, security and compliance risks can derail even the most well-planned migrations. According to recent industry reports, one-third of enterprise cloud migrations fail, often due to overlooked security gaps or compliance missteps.
The stakes are even higher for enterprises in regulated industries (finance, healthcare, government) or those with strict data residency requirements. Atlassian Cloud now supports GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, and ISO 27001, but these features must be intentionally configured—not automatically enabled.
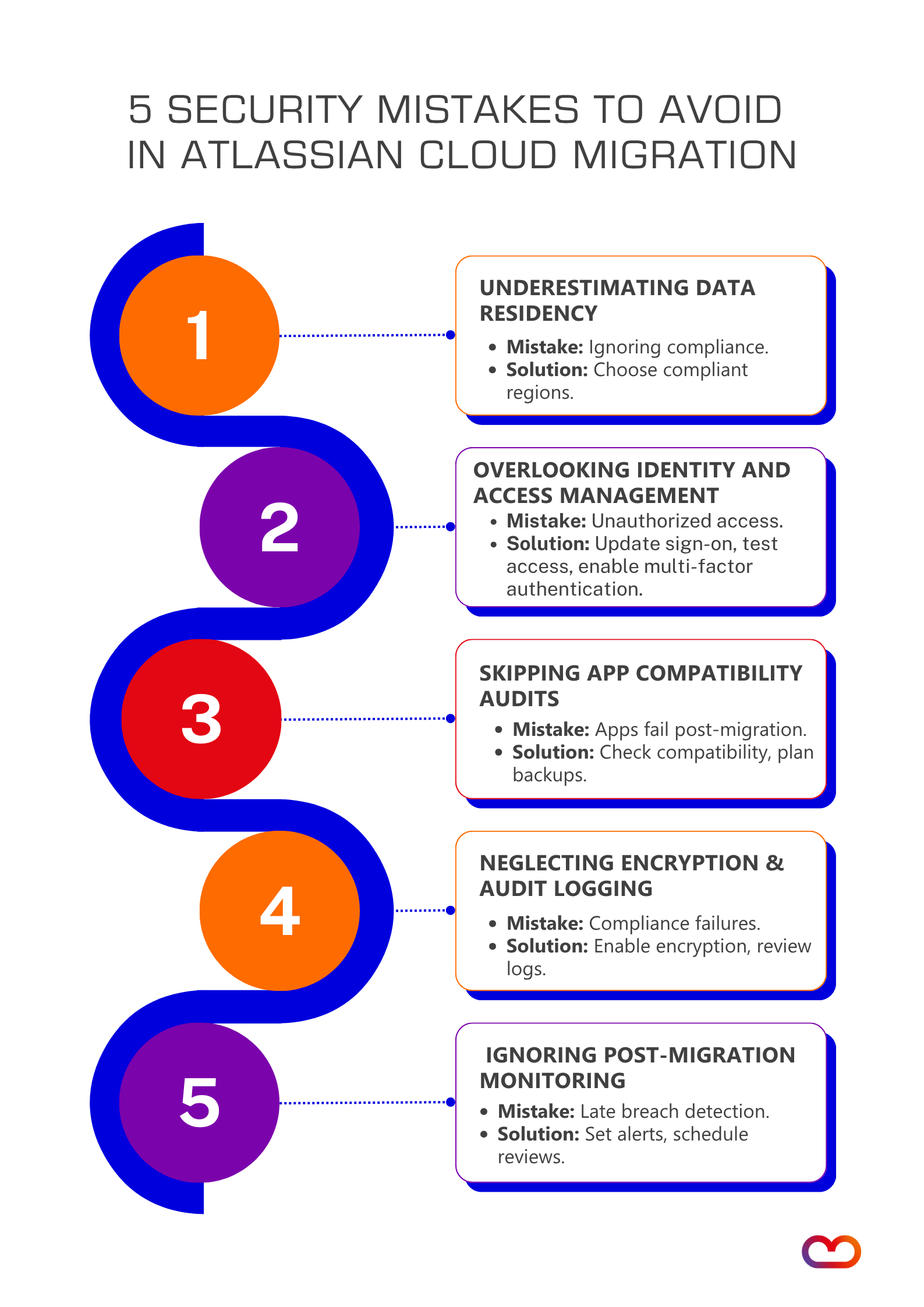
Top 5 Security Mistakes (And How to Avoid Them)
1. Underestimating Data Residency and Compliance Requirements
Mistake: Assuming all data can be stored anywhere, ignoring regional regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
Real-Life Example: A European enterprise faced regulatory fines after migrating to Atlassian Cloud without ensuring data residency in EU-compliant regions. Their oversight led to sensitive customer data being stored in non-compliant servers, violating GDPR.
Solution:
- During setup, select the right data residency region. Atlassian now offers data residency in 11 countries, but this must be chosen up front.
- Consult Atlassian’s Cloud Compliance Roadmap to track upcoming certifications and ensure your migration timeline aligns with compliance deadlines.
- Engage legal and compliance teams early to map out requirements.
2. Overlooking Identity and Access Management (IAM) Gaps
Mistake: Failing to update IAM policies, leading to unauthorized access, locked-out users, or security breaches.
Real-Life Example: A global tech company experienced 12 hours of downtime during migration when legacy Single Sign-On (SSO) configurations weren’t updated for Atlassian Cloud. The result? Hundreds of employees couldn’t access critical tools.
Solution:
- Implement SAML SSO (Security Assertion Markup Language Single Sign-On) and Atlassian Access for centralized user management and multi-factor authentication.
- Test IAM policies in a sandbox environment before full migration.
- Audit user roles and permissions to ensure least-privilege access.
3. Skipping a Comprehensive App Compatibility Audit
Mistake: Assuming all Data Center apps will work in Cloud, only to discover critical gaps post-migration.
Real-Life Example: A financial services firm rolled back their migration after discovering their custom compliance app wasn’t cloud-ready. The delay caused lost productivity and emergency consulting fees.
Solution:
- Check Cloud alternatives to your Atlassian Marketplace Data Center apps.
- Plan for alternatives if key apps aren’t available in Cloud. Consider native Atlassian features or third-party integrations.
- Work with Atlassian migration partners to identify and test apps.
4. Neglecting Data Encryption and Audit Logging
Mistake: Not enabling encryption in transit/at rest or failing to set up audit logs for compliance.
Real-Life Example: A healthcare provider failed a HIPAA audit after migrating to the cloud without enabling organization-wide audit logging. This oversight led to a six-month remediation project and a large fine.
Solution:
- Enable Atlassian Guard for enterprise-grade encryption and organization-wide audit logging.
- Configure data security policies to control how users, apps, and external parties interact with content.
- Regularly review audit logs for suspicious activity, especially during the first 30 days post-migration.
5. Ignoring Post-Migration Security Monitoring
Mistake: Treating migration as a one-time event, not a continuous process.
Real-Life Example: A tech company suffered a data breach three months after migration because it did not monitor third-party integrations. The breach exposed customer records and led to a costly settlement.
Solution:
- Use Atlassian’s built-in security dashboards to monitor user activity, app integrations, and data access.
- Set up automated alerts for unusual behavior (e.g., multiple failed login attempts, unexpected data exports).
- Schedule quarterly security reviews to assess new risks and update policies.
Migration is just the beginning. Continuous monitoring is what keeps your cloud environment secure in the long run." — Atlassian Security Team.
</blockquote>Bonus: The Mistake No One Talks About - No Rollback Plan
Mistake: Failing to define and test a rollback strategy.
Real-Life Example: A manufacturing firm lost 48 hours of productivity after a failed migration without a rollback plan. The incident delayed a major product launch and required emergency fixes.
Solution:
- Document rollback triggers (e.g., critical app failure, data loss, security breach).
- Test the rollback process in a staging environment.
- Assign a rollback owner to make swift decisions if needed.
Secure Your Atlassian Cloud Migration
Migrating to Atlassian Cloud is a transformative step for your enterprise, but security mistakes can turn opportunity into risk. By addressing data residency, IAM, app compatibility, encryption, and post-migration monitoring, you’ll not only avoid costly pitfalls but also unlock the full potential of Atlassian Cloud.